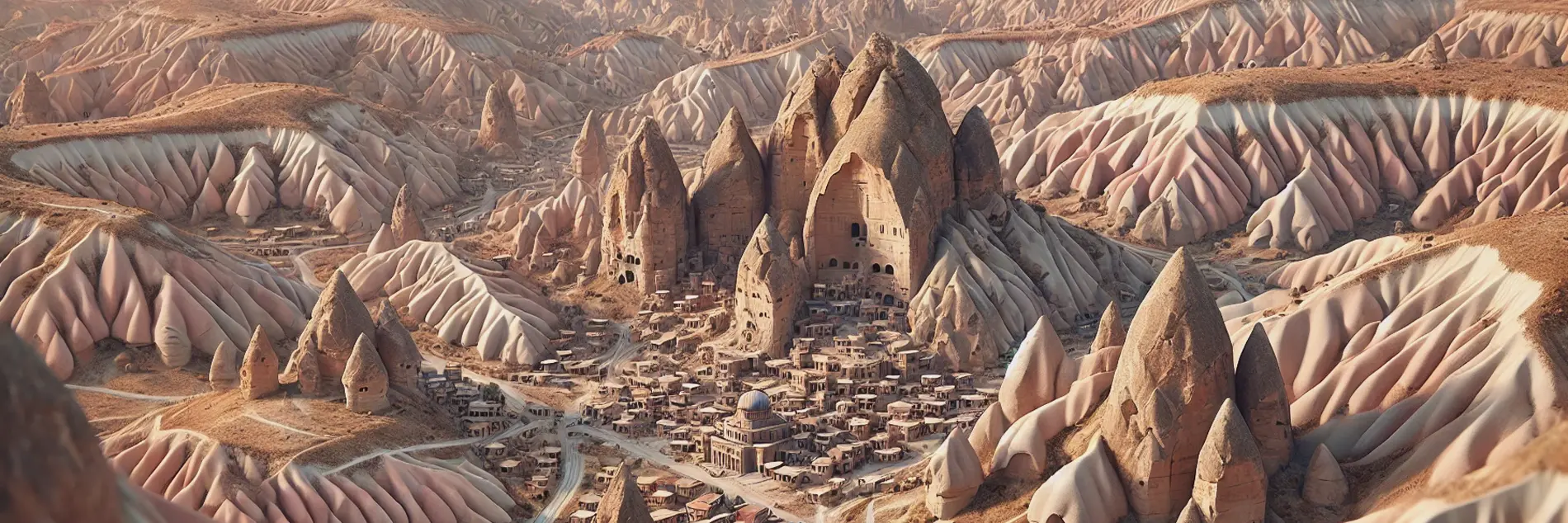

History of Cappadocia
ANCIENT CAPPADOCIA
 Cappadocia was known as Hatti in the late Bronze Age, and was the homeland of the Hittite power centred at Hattusa. After the fall of the Hittite Empire, with the decline of the Syro-Cappadocians (Mushki) after their defeat by the Lydian king Croesus in the 6th century, Cappadocia was ruled by a sort of feudal aristocracy, dwelling in strong castles and keeping the peasants in a servile condition, which later made them apt for foreign slavery. It was included in the third Persian satrapy in the division established by Darius, but continued to be governed by rulers of its own, none apparently supreme over the whole country and all more or less tributaries of the Great King.
Cappadocia was known as Hatti in the late Bronze Age, and was the homeland of the Hittite power centred at Hattusa. After the fall of the Hittite Empire, with the decline of the Syro-Cappadocians (Mushki) after their defeat by the Lydian king Croesus in the 6th century, Cappadocia was ruled by a sort of feudal aristocracy, dwelling in strong castles and keeping the peasants in a servile condition, which later made them apt for foreign slavery. It was included in the third Persian satrapy in the division established by Darius, but continued to be governed by rulers of its own, none apparently supreme over the whole country and all more or less tributaries of the Great King.
Kingdom of Cappadocia
After bringing the Persian Empire to an end, Alexander the Great tried to rule the area through one of his military commanders. But Ariarathes, a Persian aristocrat, somehow became king of the Cappadocians. AsAriarathes I (332–322 BC), he was a successful ruler, and he extended the borders of the Cappadocian Kingdom as far as to the Black Sea. The kingdom of Cappadocia lived in peace until the death of Alexander. The previous empire was then divided into many parts, and Cappadocia fell to Eumenes. His claims were made good in 322 BC by the regent Perdiccas, who crucified Ariarathes; but in the dissensions which brought about Eumenes’s death, Ariarathes II, the adopted son of Ariarathes I, recovered his inheritance and left it to a line of successors, who mostly bore the name of the founder of the dynasty.
Under Ariarathes IV, Cappadocia came into relations with Rome, first as a foe espousing the cause of Antiochus the Great, then as an ally against Perseus of Macedon. The kings henceforward threw in their lot with the Republic as against the Seleucids, to whom they had been from time to time tributary. Ariarathes V marched with the Roman proconsul Publius Licinius Crassus Dives Mucianus against Aristonicus, a claimant to the throne of Pergamon, and their forces were annihilated (130 BC). The imbroglio which followed his death ultimately led to interference by the rising power of Pontus and the intrigues and wars which ended in the failure of the dynasty.
ROMAN AND BYZANTINE PROVINCE
The Cappadocians, supported by Rome against Mithridates VI of Pontus, elected a native lord, Ariobarzanes, to succeed (93 BC); but in the same year Armenian troops underTigranes the Great entered Cappadocia, dethroned king Ariobarzanes and crowned Gordios as the new client-king of Cappadocia, thus creating a buffer zone against the encroaching Romans. It was not until Rome had deposed the Pontic and Armenian kings that the rule of Ariobarzanes was established (63 BC). In the civil wars Cappadocia was first for Pompey, then for Caesar, then for Antony, and finally, Octavian. The Ariobarzanes dynasty came to an end, a Cappadocian nobleman Archelaus was given the throne, by favour first of Antony and then of Octavian, and maintained tributary independence until AD 17, when the emperor Tiberius, who he had angered, summoned him to Rome and reduced Cappadocia to a Roman province.
Cappadocia contains several underground cities (see Kaymaklı Underground City), largely used by early Christians as hiding places before Christianity became an accepted religion. The underground cities have vast defence networks of traps throughout their many levels. These traps are very creative, including such devices as large round stones to block doors and holes in the ceiling through which the defenders may drop spears.
EARLY CHRISTIANIT
The Cappadocians, supported by Rome against Mithridates VI of Pontus, elected a native lord, Ariobarzanes, to succeed (93 BC); but in the same year Armenian troops underTigranes the Great entered Cappadocia, dethroned king Ariobarzanes and crowned Gordios as the new client-king of Cappadocia, thus creating a buffer zone against the encroaching Romans. It was not until Rome had deposed the Pontic and Armenian kings that the rule of Ariobarzanes was established (63 BC). In the civil wars Cappadocia was first for Pompey, then for Caesar, then for Antony, and finally, Octavian. The Ariobarzanes dynasty came to an end, a Cappadocian nobleman Archelaus was given the throne, by favour first of Antony and then of Octavian, and maintained tributary independence until AD 17, when the emperor Tiberius, who he had angered, summoned him to Rome and reduced Cappadocia to a Roman province.
Cappadocia contains several underground cities (see Kaymaklı Underground City), largely used by early Christians as hiding places before Christianity became an accepted religion. The underground cities have vast defence networks of traps throughout their many levels. These traps are very creative, including such devices as large round stones to block doors and holes in the ceiling through which the defenders may drop spears.
TURKISH CAPPADOCIA
Following the Battle of Manzikert in 1071, various Turkish clans under the leadership of the Seljuks began settling in Anatolia. With the rise of Turkish power in Anatolia, Cappadocia slowly became a tributary to the Turkish states that were established to the east and to the west; some of the population converted to Islam but the main Greek-Byzantine population moved to the Ionian coast. By the end of the early 12th century, Anatolian Seljuks had established their sole dominance over the region.
With the decline and the fall of the Konya-based Seljuks in the second half of the 13th century, they were gradually replaced by the Karaman-based Beylik of Karaman, who themselves were gradually succeeded by theOttoman Empire over the course of the 15th century. Cappadocia remained part of the Ottoman Empire for the centuries to come, and remains now part of the modern state of Turkey.
A fundamental change occurred in between when a new urban center, Nevşehir, was founded in the early 18th century by a grand vizier who was a native of the locality (Nevşehirli Damat İbrahim Pasha), to serve as regional capital, a role the city continues to assume to this day.
In the meantime many former Cappadocians had shifted to a Turkish dialect (written in Greek alphabet, Karamanlıca), and where the Greek language was maintained (Sille, villages near Kayseri, Pharasa town and other nearby villages), it became heavily influenced by the surrounding Turkish. This dialect of Greek is known as Cappadocian Greek. Following the 1923 population exchange between Greece and Turkey, the language is now only spoken by a handful of the former population’s descendants in modern Greece.


